Apr 14, 2025 /Level: Beginners /Avg reading time: 14 minutes
Imagine a global marketplace, operating 24 hours a day, five days a week, where trillions of dollars change hands every single day. This isn’t the stock market, nor is it a physical exchange building. This is the Forex market, or the foreign exchange market, the largest and most liquid financial market in the world. If you’ve ever wondered, “Forex what is it?”, you’ve come to the right place. This comprehensive guide will break down the meaning of Forex, explain what is Forex trading, and provide a clear definition of the Forex market for complete beginners.
Understanding Forex and how does Forex work? might seem daunting at first, but the core concept is surprisingly straightforward. It’s essentially the buying and selling of currencies. Just as individuals and businesses need to exchange currencies when traveling or conducting international trade, the Forex market facilitates these transactions on a massive scale. Learning about Forex can offer new insights into global economics and potential investments. However, it’s crucial to understand the fundamentals and inherent risks before starting.
So, let’s dive into the basics of Forex. We’ll explain it in a way that’s easy for anyone to understand.
Forex What is it? (Explained for Beginners)
As mentioned, Forex is an abbreviation for Foreign Exchange. Let’s break down each word to gain a clearer understanding. “Foreign” simply refers to something originating in or belonging to a country other than one’s own. “Exchange” in this context signifies the act of trading or swapping one thing for another. Therefore, foreign exchange literally means the exchange of one country’s currency for another.
At its heart, the Forex market is the mechanism that allows individuals, businesses, and financial institutions to convert one currency into another. Whether a multinational corporation needs to pay its employees in a different country, a tourist wants to exchange their home currency for the local currency of their destination, or a speculator aims to profit from fluctuations in currency exchange rates, the Forex market provides the platform for these transactions. Understanding this fundamental principle is the first step in truly grasping Forex what is it.
How Does the Forex Market Work?
The core of the FX market revolves around the concept of currency pairs. Unlike buying a single stock, in Forex, you are always trading one currency against another. This is because the value of a currency is always relative to another currency. Think of it as a comparison – the price of the Euro isn’t absolute; it’s expressed in terms of how many US dollars (or other currencies) it takes to buy one Euro.
The Concept of Currency Pairs:
The way these relationships are expressed is through currency pairs. The first currency listed in the pair is called the base currency, and the second currency is the quote currency (also known as the counter currency). For example, in the major currency pair EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar), the Euro (EUR) is the base currency, and the US Dollar (USD) is the quote currency. The exchange rate of this pair indicates how many US dollars are needed to buy one Euro.
The price quoted (e.g., 1.1000) tells you how many units of the quote currency (USD) are needed to buy one unit of the base currency (EUR). So, EUR/USD at 1.1000 means 1 Euro costs 1.1000 US Dollars. Importantly, you’re always simultaneously buying and selling currencies.
When you trade a currency pair, you are essentially simultaneously buying one currency and selling the other. For instance, if you believe the base currency will strengthen relative to the quote currency, you would “buy” the pair (go long). Conversely, if you anticipate the base currency weakening against the quote currency, you would “sell” the pair (go short).
Types of currency Pairs
Currency pairs are categorized:
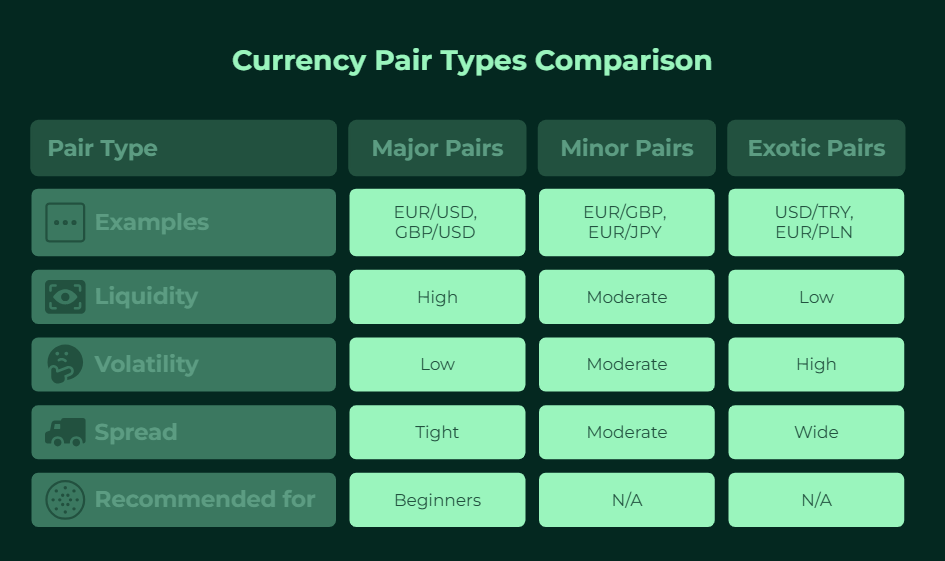
- Major Currency Pairs: These involve the US dollar (USD) paired with other major currencies (like EUR, GBP, JPY, CHF, CAD, AUD, NZD). Examples: EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/JPY. They are the most traded and generally have the highest liquidity (ease of buying/selling) and tightest spreads (lower transaction costs). For this reason, many beginners focus on these. What are the best currency pairs to trade for beginners? Often, majors like EUR/USD are recommended due to liquidity and available information.
- Minor Currency Pairs (Crosses): These pairs feature major currencies excluding the USD. Examples: EUR/GBP, EUR/JPY, GBP/AUD.
- Exotic Currency Pairs: These pair a major currency with one from an emerging or smaller economy. Examples: USD/TRY (Turkish Lira), EUR/PLN (Polish Zloty). On the negative side, they are less liquid, more volatile, and usually have wider spreads.
Understanding Exchange Rates:
The exchange rate of a currency pair is constantly fluctuating. These fluctuations are driven by a multitude of factors, which we’ll delve into later. The exchange rate represents the price at which one currency can be exchanged for another at a specific point in time. This price is dynamic and changes based on the forces of supply and demand. If there is a high demand for a particular currency and a limited supply, its value will likely increase, leading to changes in currency exchange rates. Conversely, if the supply of a currency outweighs the demand, its value will likely decrease.
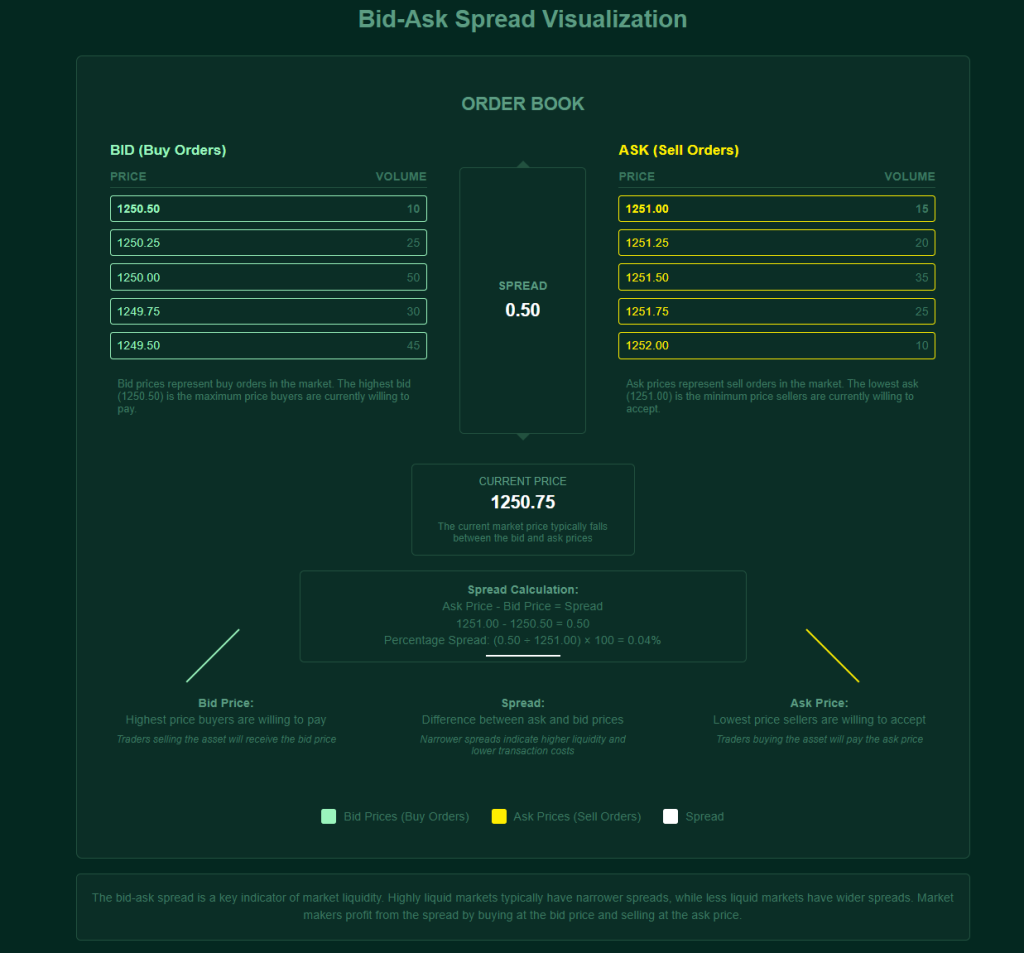
Forex quotes always show two prices:
- Bid Price: The price at which the broker is willing to buy the base currency from you (i.e., the price at which you can sell).
- Ask Price: The price at which the broker is willing to sell the base currency to you (i.e., the price at which you can buy). The ask price is always slightly higher than the bid price.
Who Participates in the Forex Market?
The global currency market is a diverse ecosystem with various participants, each playing a crucial role:
- Central Banks: These institutions, such as the Federal Reserve in the US or the European Central Bank, are major players. They manage their countries’ currency reserves, implement monetary policy (like adjusting interest rates). Additionally, they may also intervene in the market to stabilize their currency or achieve specific economic goals.
- Commercial Banks: Large banks facilitate currency exchange for their clients and also trade on their own accounts. They are key intermediaries in the FX market.
- Investment Funds: Hedge funds, mutual funds, and other institutional investors actively trade currencies to generate returns.
- Corporations also participate. Multinational companies buy and sell currencies for various reasons. These include paying for international goods/services, repatriating profits, and managing foreign exchange risk.
- Retail Traders: Lastly, Retail traders are individuals trading currency pairs via online brokers or prop firms. Their aim is to profit from exchange rate movements. This is the segment that beginner traders typically fall into.

The Decentralized Nature:
Unlike stock markets that typically have a central physical location (like the New York Stock Exchange), the Forex market is decentralized. It’s a global network of banks, financial institutions, and individual traders connected electronically. This over-the-counter (OTC) nature contributes to its 24/5 operation, as trading flows from one financial center to another across different time zones.
Essential Forex Terminology for Beginners
To truly understand Forex explained, you need to familiarize yourself with some essential FX terminology:
- Pips: A pip (Price Interest Point) is the smallest unit of price movement in most currency pairs. Typically, it’s the fourth decimal place (e.g., in EUR/USD, a move from 1.1000 to 1.1001 is a one pip increase). Understanding pips is crucial for calculating potential profits or losses.
- Lots: Trading volume in Forex is standardized into lots. A standard lot is 100,000 units of the base currency. Smaller denominations like a mini lot (10,000 units) and a micro lot (1,000 units) are also commonly available, allowing traders with smaller accounts to participate.
- Bid and Ask Price: When looking at a currency pair quote, you’ll see two prices: the bid price and the ask price. The bid price is the price at which you can sell the base currency, and the ask price is the price at which you can buy the base currency.
- Spread: The difference between the bid price and the ask price is called the spread. This is essentially how brokers make their money (indirectly acting as a transaction fee). A tighter spread generally means lower trading costs.
- Leverage in Forex: Leverage allows traders to control a larger position in the market with a smaller amount of their own capital. It’s expressed as a ratio (e.g., 1:50, 1:100). While leverage can amplify potential profits, it can also significantly magnify losses, making risk management paramount.
- Margin in Forex: Margin is the amount of capital required in your account to open and maintain a leveraged position. It’s not a fee but rather a portion of your account balance that is “set aside” as collateral.
- Long Position: Buying a currency pair with the expectation that its value (the base currency relative to the quote currency) will rise.
- Short Position: Selling a currency pair with the expectation that its value will fall.
Forex Pip Calculator
A pip (Price Interest Point) is the smallest unit of price movement in most currency pairs. For most pairs, it’s the fourth decimal place (0.0001), except for pairs involving JPY where it’s the second decimal place (0.01).
Why Do Exchange Rates Change? (Understanding the Drivers)
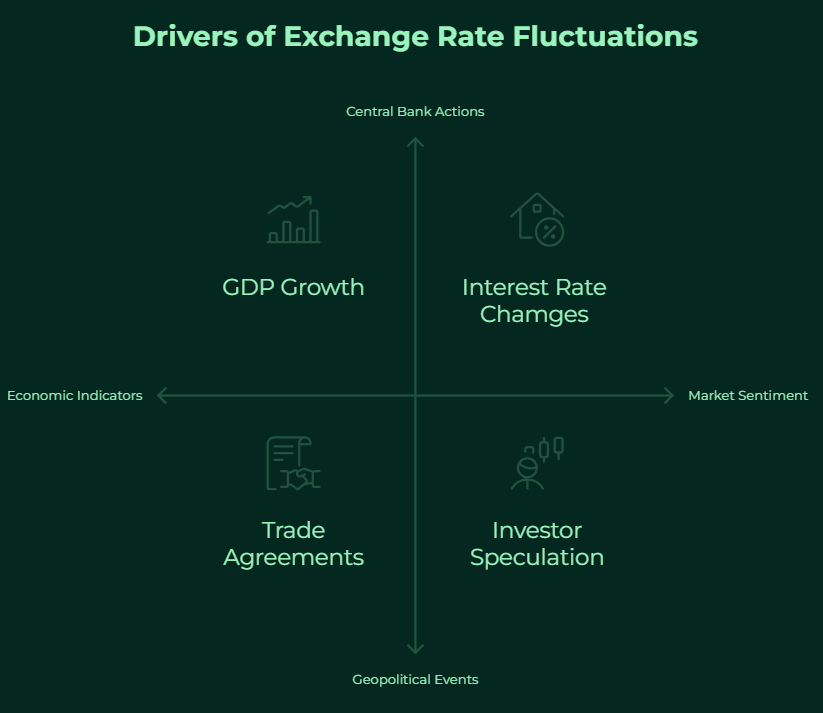
The constant fluctuations in exchange rates are what create opportunities (and risks) in the Forex market. Several key factors drive these movements:
- Economic Indicators: The health and performance of a country’s economy significantly influence its currency value. Key economic indicators such as inflation rates, interest rates set by central banks, Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth, employment figures, manufacturing data, and retail sales reports can all impact currency valuations. Positive economic data typically strengthens a currency, while negative data can weaken it.
- Geopolitical Events: Secondly, political stability, elections, trade agreements, international conflicts, and other geopolitical events can create uncertainty and volatility in the currency markets. Without doubt, unexpected events can lead to rapid and significant exchange rate shifts.
- Market Sentiment: The overall feeling or attitude of investors towards a particular currency or the broader market plays a significant role. Positive sentiment can drive demand and push currency values higher. Negative sentiment often leads to selling pressure and price declines. Speculation by traders also contributes to market sentiment.
- Central Bank Actions: As mentioned earlier, central banks wield considerable influence over their national currencies. Their monetary policy decisions, such as adjusting interest rates, implementing quantitative easing (or tightening), and direct market interventions, can have a profound impact on exchange rates.
Getting Started with Forex Trading (Practical Steps for Beginners)
Forex trading involves speculating on the future direction of exchange rates with the goal of making a profit. Traders aim to buy a currency pair if they believe the Base currency will appreciate against the Quote currency, or sell a currency pair if they anticipate the base currency will depreciate.
This trading activity takes place through online trading platforms provided by online Forex brokers and prop trading firms. These platforms offer real-time price quotes, charting tools, and the ability to execute trades. Traders use various analytical techniques, including technical analysis (studying price charts and candlestick patterns) and fundamental analysis (analyzing economic and political news), to try and predict future price movements.
Now, how do you actually start trading, especially if you don’t have substantial capital of your own? While the traditional route involves opening an account with a retail Forex broker and trading your own funds, an increasingly popular alternative, particularly appealing to dedicated beginners, is seeking a funded account through a proprietary trading firm (prop firm) like Leveraged.
How to Start Forex Trading in 7 Steps
Instead of depositing your own large sum, prop firms offer a different model: they provide capital to traders who can prove their ability to trade profitably and manage risk effectively, usually through a simulation challenge. Here’s a practical roadmap for exploring this path:
- Education is Paramount: Before risking a single dollar, invest time in learning. Read guides like this one, explore online courses, watch webinars, and understand the basics of Forex. Don’t rush this step but rather learn about Forex thoroughly.
- Develop a clear trading plan (entry/exit rules, pairs to focus on). Don’t trade randomly. Your plan should outline:
- What currency pairs you’ll trade.
- What conditions trigger a buy or sell decision (based on simple analysis).
- How much you’ll risk per trade (e.g., 1-2% of your capital).
- Where you’ll place your stop-loss (an order to automatically close a losing trade at a predefined level) and take-profit orders.
- Take the Simulation Challenge: Once prepared and clear on the rules, pay the fee and begin the challenge. Treat the evaluation account like real capital. Focus intensely on executing your plan, adhering strictly to the risk parameters, and achieving the profit target without breaching any rules.
- Perform Consistent Market Analysis: Throughout the challenge (and if funded), continuously perform market analysis. Use your chosen methods—whether technical analysis (charts, indicators), fundamental analysis (economic news, factors affecting currency prices, central banks activity), or a combination—to identify trading opportunities aligned with your plan.
- Execute Trades with Discipline: Place your trades based on your analysis and trading plan. Avoid impulsive decisions or deviating from your strategy under pressure.
- Monitor Performance and Adhere Strictly to Rules: Once trades are live (in the challenge or funded account), monitor them according to your plan. Critically, always keep track of your daily and overall drawdown. Avoid trades that could put you close to breaching these limits, as even one violation usually means failing the challenge or losing the funded account.
- Learn from Your Performance (Especially Challenges): Whether you pass or fail an evaluation, analyze your performance rigorously. Keep a trading journal. What worked? Where did you deviate? Did you follow your risk rules? Understanding your strengths and weaknesses, particularly under the pressure of evaluation rules, is vital for growth and future success in the prop firm environment.
It’s important to understand that while there’s potential for profit in Forex trading, it also involves significant risk. The high degree of leverage available can amplify both gains and losses.
Position Size Calculator
Pips at risk: 0
Position sizing is a risk management technique that determines how many units of a currency pair to trade based on your account size, risk tolerance, and the distance between your entry point and stop loss. Proper position sizing helps protect your capital by ensuring you never risk more than a predetermined percentage of your account on any single trade.
Risks Associated with Forex Trading
Before considering any form of Forex trading, it’s absolutely crucial to be aware of the inherent risks:
- Volatility: The Forex market is known for its high volatility. Exchange rates can fluctuate rapidly and unpredictably in response to economic news, political events, and market sentiment. Consequently, this volatility can lead to significant losses in a short period.
- Leverage Risk: While leverage can magnify potential profits, it also magnifies potential losses to the same extent. Trading with high leverage means that even small adverse price movements can result in substantial losses that may exceed your initial investment.
- Complexity: While the basic concept of currency exchange is simple, understanding the intricate factors that drive exchange rate movements and developing profitable trading strategies requires significant learning, analysis, and experience.
- Importance of Education and Risk Management: Success in Forex trading is not guaranteed and requires a strong foundation in Forex basics, a well-defined trading plan, and robust risk management strategies. Beginners should prioritize education and practice on demo accounts before risking real capital.
Can You Really Make Money Trading Forex?
This is the question on many beginners’ minds: Can you really make money trading Forex? The straightforward answer is yes, it is possible to make money trading Forex. However, it’s crucial to temper this with a healthy dose of realism and understand that it’s not a guaranteed path to riches.
Here’s a more nuanced look at the potential for profitability:
- Success Stories Exist: There are undoubtedly individuals and professional traders who have achieved significant financial success through Forex trading. They often possess a deep understanding of the market, have well-defined trading strategies, practice disciplined risk management, and dedicate a considerable amount of time and effort to honing their skills.
- Leverage Amplifies Both Gains and Losses: The inherent leverage in Forex allows traders to control larger positions with less capital, which can lead to substantial profits on successful trades. However, as emphasized earlier, this same leverage can equally amplify losses if trades go against them.
- Requires Skill, Knowledge, and Discipline: Thirdly, consistently making money in Forex trading is not a matter of luck. It demands strong market understanding, including technical and fundamental analysis. What’s more, you also need the ability to develop and follow a profitable strategy. Emotional discipline is also paramount to avoid impulsive decisions driven by fear or greed.
- Time and Effort Commitment: Successful Forex trading often requires a significant time commitment for learning, analyzing the markets, and executing and managing trades. It’s not typically a “get rich quick” scheme or a passive income source in the initial stages.
- The Prop Firm Advantage: Prop firms like Leveraged remove the barrier of needing large personal capital. If you can demonstrate consistent profitability and risk management during the challenge, you gain access to significant capital, making substantial profit potential (like the 80% share) more attainable than starting small with your own funds.
How To Make Money Forex Trading
Here’s how profit (and loss) occurs:
Going Long (Buying): If you believe the base currency will strengthen against the quote currency (e.g., you think the Euro will rise against the US Dollar), you buy the EUR/USD pair. If the price goes up, you can sell it back at a higher price for a profit.
Going Short (Selling): If you believe the base currency will weaken against the quote currency (e.g., you think the British Pound will fall against the Japanese Yen), you sell the GBP/JPY pair. If the price goes down, you can buy it back at a lower price, profiting from the difference.
In conclusion, while making money in Forex trading is achievable, it is a challenging endeavor with a high risk of capital loss. Success is typically reserved for those who are willing to invest the time and effort to educate themselves, develop a sound trading strategy, practice strict risk management, and maintain psychological discipline.
Trading with a funded account means your potential earnings are based on a percentage (like Leveraged’s 80%) of the profits generated on a much larger capital base than most beginners could access alone.
Is Forex Trading Right for You? (Managing Expectations)
After understanding “Forex what is it,” how it works, the potential for profit, and the significant risks involved, the next logical question is: Is Forex trading right for you? This is a personal decision that depends on your individual circumstances, personality, and financial goals. Consider the following questions to help you assess if Forex trading aligns with your profile:
- What is your risk tolerance?
- Do you have sufficient disposable income?
- Are you willing to dedicate time to learning and analysis?
- Are you emotionally disciplined?
- Do you have realistic expectations?
- Do you understand the concept of leverage?
- Are you comfortable with uncertainty?
- Are you motivated by the potential for financial independence and growth?
Final Words
So, Forex what is it in essence? It’s the global, decentralized marketplace where currencies are bought and sold, facilitating international trade and investment. Understanding the meaning of Forex, how does Forex work, the role of currency pairs and exchange rates, and the key terminology are fundamental first steps.
While Forex trading holds profit potential, the risks, especially leverage, are real. Traditionally, starting required significant personal capital. However, the landscape is changing.
Proprietary trading firms like Leveraged provide a modern pathway. Leveraged empower dedicated traders, even beginners, by offering access to substantial capital (up to $1 Million) and the chance to keep 80% of the profits, provided you can first prove your skills and discipline in their simulation challenge. You trade Leveraged’s capital, minimizing your personal financial risk while benefiting from Leveraged’s support structure, including advanced AI tools, education, and a community.
You’ve learned the basics of Forex and the potential it holds. But knowing isn’t enough – doing is what counts. Worried about needing huge amounts of personal capital to start trading effectively?
Ready to leverage your trading skills?
Click the button below and stop dreaming about trading significant capital – start proving you can.